Dictionaries in Python are mutable, unordered collections that store
key-value pairs. Each key in a dictionary must be unique, and the keys are used
to access the associated values. Here’s a comprehensive guide to working with
dictionaries in Python:
Creating Dictionaries
You can create dictionaries using curly braces {} with key-value pairs separated by colons.
# Creating an empty dictionary
empty_dict = {}
# Creating a dictionary with some key-value pairs
student = {
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 20,
"courses": ["Math",
"Computer Science"]
}
Accessing Values
You can access values in a dictionary by using their keys.
# Accessing values by key
print(student["name"]) # Output: John Doe
print(student["age"]) # Output: 20
print(student["courses"]) # Output:
['Math', 'Computer Science']
Modifying Dictionaries
You can modify the values associated with a specific key, add new
key-value pairs, and delete existing ones.
Changing Values
# Changing the value
associated with a key
student["age"] = 21
print(student["age"]) # Output: 21
Adding Key-Value Pairs
# Adding a new key-value pair
student["grade"] = "A"
print(student) # Output: {'name': 'John Doe',
'age': 21, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science'], 'grade': 'A'}
Removing Key-Value Pairs
# Removing a key-value pair using del
del student["grade"]
print(student) # Output: {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 21, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science']}
# Removing a key-value pair using pop()
age = student.pop("age")
print(age) #
Output: 21
print(student) #
Output: {'name': 'John Doe', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science']}
Dictionary Methods
Dictionaries come with several built-in methods.
keys(), values(), and items()
These methods are used to access the keys, values, and key-value pairs in
the dictionary.
print(student.keys())
# Output: dict_keys(['name', 'courses'])
print(student.values()) # Output: dict_values(['John Doe',
['Math', 'Computer Science']])
print(student.items())
# Output: dict_items([('name', 'John Doe'), ('courses', ['Math',
'Computer Science'])])
update()
This method updates the dictionary with key-value pairs from another
dictionary or from an iterable of key-value pairs.
# Updating a dictionary with another dictionary
student.update({"age": 21, "grade":
"A"})
print(student) # Output: {'name': 'John Doe', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science'], 'age': 21, 'grade': 'A'}
# Updating a dictionary with an iterable of key-value pairs
student.update([("age", 22), ("grade",
"B")])
print(student) #
Output: {'name': 'John Doe', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science'], 'age':
22, 'grade': 'B'}
get()
This method returns the value for a specified key if the key is in the
dictionary, otherwise it returns a default value.
print(student.get("name")) # Output: John Doe
print(student.get("grade")) # Output: B
print(student.get("address", "Not
Available")) # Output: Not
Available
popitem()
This method removes and returns the last inserted key-value pair as a
tuple.
last_item = student.popitem()
print(last_item) #
Output: ('grade', 'B')
print(student) #
Output: {'name': 'John Doe', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science'], 'age':
22}
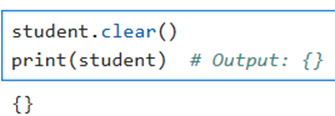
clear()
This method removes all items from the dictionary.
student.clear()
print(student) #
Output: {}
Summary
- Creating Dictionaries: Use curly braces {} with key-value pairs separated
by colons.
- Accessing Values: Use keys to access values.
- Modifying Dictionaries: Add, change, and remove
key-value pairs.
- Dictionary Methods: Use methods like keys(), values(), items(), update(), get(), popitem(), and clear().
- Iterating Over Dictionaries: Iterate over keys, values, and
key-value pairs.
Dictionaries are highly versatile and useful for various applications,
including data representation, counting, and simple databases. Mastering
dictionaries will greatly enhance your ability to work with structured data in
Python.









Comments
Post a Comment